Resultant Velocity Formula Projectile Motion
Mention one assumption made. Uniform motion constant velocity Equations.

Projectile Motion Calculator Excel Physics Projectile Motion Excel Graphing
Total Time of Flight.

Resultant velocity formula projectile motion. Vyusin - gt At tT2 vy 0 0 usin - gT2. Related Threads on Resultant Velocity of a Projectile Velocity of a Projectile. Formula for Projectile Motion.
Resultant displacement s 0 in Vertical direction. V vx2 vy2 u2 g2 t2. For example if the velocities of particles A and B are v A and v B.
Definition of projectile motion. The vertical velocity component Vy is equal to V sin . Where V x is the velocity along the x-axis V xo is Initial velocity along the x-axis V y is the velocity along the y-axis V yo is initial velocity along the y-axis g is the acceleration due to gravity.
This is equal to the time taken by the projectile to return to ground. Range A projectile launched with specific initial conditions will travel a predictable horizontal displacement before striking the. The resultant velocity at impact and the angle this makes with the vertical.
Displacement initial velocity final velocity2change in time. The above equation is of the form y Ax Bx2 and represents a parabola. Physics Study Notes Lesson 5 Projectile Motion Mr.
SX S0X vX t where S0X is the initial horizontal location. Gt2 2 uyt sy Here u y u sin and s y 0 ie. Uniform motion constant velocity Formula for horizontal location of a projectile at any time t.
Gt2 2t u sin . Horizontal component of projectile motion. Grab the opportunity and understand the concept of Projectile Motion better using the Projectile Motion Formulas List provided.
If the vertical velocity component is equal to 0 then its the case of horizontal projectile motion. The Attempt at a Solution. That is f m a.
5 in your text book Students will be able to. In other words any motion in two dimensions and only under the effect of gravitational force is called projectile motion. Angular Projectile motion is symmetrical about the highest pointThe object will reach the highest point in time T2At the highest pointthe vertical component of velocity vy becomes equal to zero.
Magnitude of resultant velocity at any point P v 2 v x2 v y2 So the equation of the horizontal projectile velocity is. Thus the path of a projectile is a parabola. Velocity of projectile at any instant is the resultant velocity that the projectile has at the given instant.
Homework Equations SUVAT equations. Break the initial resultant velocity vector into horizontal and vertical components. Velocity v 1 of swimmer velocity v 2 of current and resultant velocity v 1 v 2 Example 4 Newtons Second Law.
After substituting all the known values in I get the result 26017 which is only slightly different from Sals result. Trajectory is the relation between instantaneous coordinates Here x y coordinate of the particle. 1Add smaller vectors going in the same direction to get one large vector for that direction 2Draw a resultant vector for a given vertical and horizontal vector 3Calculate the magnitude of a resultant vector based on the magnitudes of the horizontal and vertical vectors.
Resultant velocity of the projectile at any instant t1 At C the velocity along the horizontal direction is ux u cos and the velocity along the vertical direction is uy u2. Break the initial resultant velocity vector into horizontal and vertical components. T is the time taken.
The resultant velocity at any point in a projectile is VxVy where Vx is horizontal velocity and Vy is vertical velocity at that point. Projectile Motion is a form of motion that is experienced by an object thrown into air which is subjected to acceleration due to gravity. Relative velocity is the vector difference between the velocities of two objects in the same coordinate system.
Any object that is thrown into the air with an angle theta is projectile and its motion called projectile motion. The path followed by a particle here projectile during its motion is called its Trajectory. We need to find the velocity component along X.
Three vectors - V Vx and Vy - form a right triangle. For finding different parameters related to projectile motion we can make use of differential equations of motions. Therefore by using the Equation of motion.
In the case of a projectile the instantaneous velocity vector would be the resultant of a constant velocity horizontal motion and an accelerated velocity vertical motion. If additionally 90 then its the case of free fall. EQUATION OF TRAJECTORY.
Following are the formula of projectile motion which is also known as trajectory formula. Maximum height reached by the projectile. Newtons famous Second Law of Motion asserts that the sum f of the vector forces on an object is equal to the scalar multiple of the mass m of the object times the vector acceleration a of the object.
Horizontal component of projectile motion. For calculating the final vertical velocity is it possible to use the formula.

Physics Motion Graphs Motion Graphs Solving Quadratic Equations Graphing Quadratics

Math Principles Resultant Of Forces And Components Force Physics Components

The Fnet M A Concept Builder Targets The Concept Of Net Force And Its Relationship To Mass And Acceleration Learn Physics Projects Body Diagram Newtons Laws

Trajectory Angle Launched Projectiles Concept Builder A Numerical Approach To Projectile Motion Includes Thr Motion Activities Projectile Motion Activities

Math Principles Projectile Motion Problems Projectile Motion Motion Math

The Vector Addition Does Order Matter Interactive Allows A Learner To Explore Whether Changing The Order In Which Four Ve Ap Physics Physics Physics Concepts

Math Principles Rate Distance And Time Problems 9 Basic Algebra Still Water Math

Which One Doesn T Belong Concept Builder A Tool That Challenges Students To Use An Understanding Of Pro Which One Doesnt Belong Body Diagram Progress Report

Projectile Motion Of A Tennis Ball Teaching Resources Projectile Motion Engineering Science Tennis Ball

Resultat De Recherche D Images Pour Long Jump Take Off Projectile Motion Learning Science Worksheets

Trajectory Horizontally Launched Projectiles Concept Builder An Interactive Tool That Takes A Numerical Approach T Interactive Tools Progress Report Concept

Kinematics Of Particles Part Ii Curvilinear Motion And Projectile Moti Math Equations Projectile Motion Particles

Finding Resultant Force From 2 Forces At 0 To 90 Degree Physics And Mathematics 90 Degrees Physics

Component Addition Concept Builder Challenges Learners To Apply Vector Principles And Mathematics In Order To Determine The M Concept How To Apply Mathematics

Horizontally Launched Projectiles Problem Solving Physics Classroom Problem Solving Word Problems

Initial Velocity Components Physics And Mathematics Physics Classroom Physics Topics

Vectors And Projectile Motion And Worked Examples Projectile Motion Motion Example
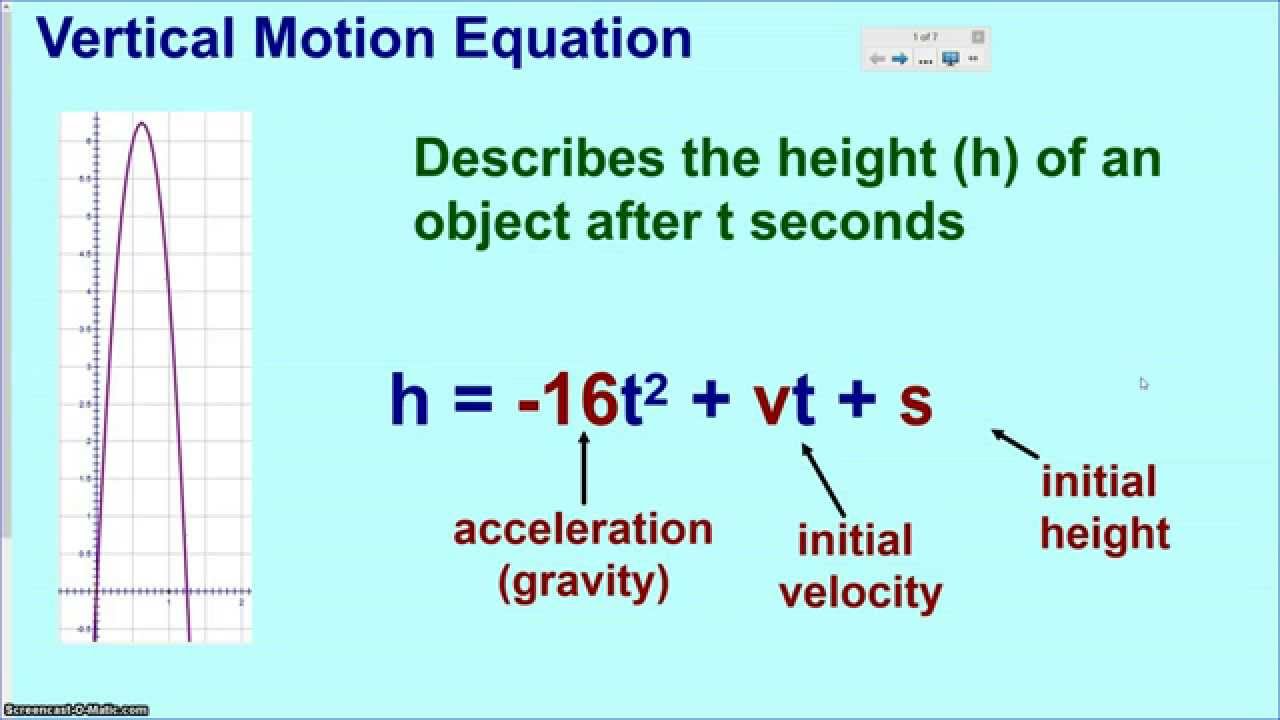
Vertical Projectile Motion Graphing Quadratics Word Problem Worksheets Math Problem Solving Strategies

Physics 3 5 4b Projectile Practice Problem 2 Physics Projectile Motion Practice
Post a Comment for "Resultant Velocity Formula Projectile Motion"