How To Find Resultant Intensity
The intensity of the light originating from the first slit is double the intensity from the second slit. If intensity due to each source is I0 12 Wm2 at P and d22D 3 calculate the resultant intensity at P.

Derive Expression For Intensity At Any Point On The Observation Screen In Young S Double Slit Experiment Hence Write The Condition Physics Wave Optics 13451956 Meritnation Com
If phase angle is zero then the equation becomes.
How to find resultant intensity. If two identical waves are traveling in the same direction with the same frequency wavelength and amplitude. The total power is twice that of one source. Solving the resultant amplitude equation for intensity After rearranging the terms the generic equation for intensity becomes The resultant intensity will change by changing the values of the phase angle otherwise it will remain the same.
Often however we know the forces that act on an object and we need. In this case as rays coming from S2 and S3 are out of phase they are simply being cancelled and the net intensity at P is due to S1 only and is equal to I. 1210 p r p I r p s r .
After making the phasor diagram calculate the resultant treating them as vectors. Intensity will depend on the strength and amplitude of a wave. How do you find the resultant of two waves.
The formula for intensity is articulated by Where I is the intensity P is the power and A is the area of cross-section. Consider interference between two sources of intensity I and 4I. For constructive interference I R I 1 I 2 2 where the waves are superposed in same phase.
For 70 dB SPL A 20 10 6 2 10 70 20 008944 P a. When 0 crest to crest and trough to trough then cos 2 1. A 20 10 6 2 10 L 20.
BUT differ in phase the waves add together. Calculate the magnitude and position of the resultant load. Resultant Amplitude and Intensity of Two waves in Wave Optics for JEE and NEET is the topic of this physics video lesson.
Recall that the intensity of the old amplitude was I X 2. In this case the resultant intensity is maximum. Intensity is defined to be the power per unit area carried by a wave.
A single slit of width 01 mm is illuminated by a mercury light of wavelength 576 nm. Find the intensity at a angle to the axis in terms of the intensity of the central maximum. The relationship between sound level in dB SPL and the amplitude of the sinusoidal pressure wave in pascals is.
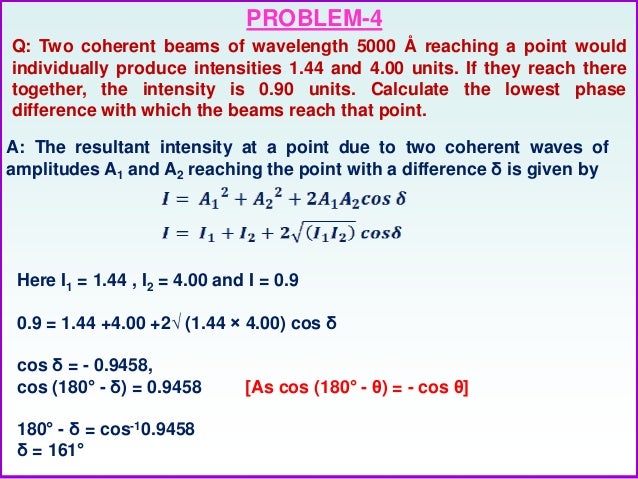
Convert each sound level L to the corresponding amplitude A of the sinusoidal pressure wave. Take the ratio of new intensity to the old intensity. The resultant intensity is I I1 I2 2 I1 I2 Cos .
A reduction of the sound power level of the sound source by 6 dB is resulting in a reduction of the sound pressure level and the sound intensity level at the location of the receiver by also 6 dB even if the sound power drops to a factor of 025 the sound pressure drops to a factor of 05 and the sound intensity drops to a factor of 025. At the point of constructive interference the resultant amplitude becomes 2 1 A. Resultant force is 13 of the length of the load from the larger end 5 kNm 4 m 4 m x m x x b m m 3 4 4 3 1 0 3 1 0 133 m 10 kN.
Problem 238 The beam AB in Fig. Intensity is represented as I. Where the two add constructively the field is twice as big so the energy density is four times as big.
Each wave is a periodic disturbance. Calculate the new amplitude. For example if a box of 15 kg is subject to 5 forces which make it accelerate 20 ms 2 north-west then the resultant force is directed north-west and has the magnitude equal to 15 kg 20 ms 2 30 N.
Power is the rate at which energy is transferred by the wave. Where they add destructively the result is zero. P-238 supports a load which varies an intensity of 220 Nm to 890 Nm.
Find out resultant intensity where phase difference is i. The amplitudes of the two interfering waves are in the ratio 2. Integral Method The magnitude of the resultant force is given by the integral of the curve defining the force wx 5 m 2 m F kN F x F w x dx x dx r m r m x m x r.
Which indicates that the resultant force R has the same direction as a and has magnitude equal to the product m a. In equation form intensity I is I P A I P A where P is the power through an area A. Waves that combine together in phase add up each together and gets high intensity.
1 say 2 A and A. At the rigid surface of the sphere where r R we have the boundary condition of zero normal velocity. Consider the interference at P between waves emanating from three coherent sources in same phase located at S1 S2 and S3.
I X 2 2 X 2 4 X 2. The width of the central peak in a single-slit diffraction pattern is 50 mm. Using the principle of superposition of fields we now express the resultant field p r as the sum of the incident and scattered fields.
Recall that intensity is proportional to amplitude squared. The SI unit for I is Wm 2.

Superposition Of Waves Principle Constructive Destructive Interference

Chapter 11 Superposition Of Light Wave When Two Waves

If Intensity Of Each Wave In The Observed Interface Pattern Is Young S Double Slit Experiment Is I0 Then For Some Point P Where The Phase Difference Is Intensity I Will

Principle Of Superposition Of Wave Resultant Intensity Superposition Superposition Of Waves Youtube

Interference Fringe Shift And Problems Iit Jee And Neet Physics
Derive The Expression For The Intensity At A Point Where Interference Of Light Occurs Arrive At The Conditions For The Maximum And Zero Intensity
Resultant Amplitude And Intensity Myrank

Superposition Of Waves Principle Constructive Destructive Interference

Superposition Of Waves Principle Constructive Destructive Interference

Resultant Amplitude An Intensity At Any Point In Double Slit Experiment Youtube

How To Calculate Intensity Of Resultant Wave Q139 Principle Of Superposition Wave Optics Youtube

10b11ph111 Wave Physical Optics Modern Physics Interference Ppt Download

Numerical Question Of Finding Intensity Of Resultant Wave In Urdu Hindi Youtube

If Intensity Ratio Of Two Interfering Waves Is 9 1 The Ratio Of Maximum To Minimum Amplitude Of Resultant Wave Is

Principle Of Superposition Of Wave Resultant Intensity Superposition Superposition Of Waves Youtube

Resultant Amplitude And Intensity Of Two Waves In Wave Optics For Jee And Neet Youtube

If The Intensity Of The Waves Observe By Two Coherent Sources Is I Than The Intensity Of Resultant Wave In Physics Wave Optics 12840355 Meritnation Com


Post a Comment for "How To Find Resultant Intensity"