Resultant Velocity Khan Academy
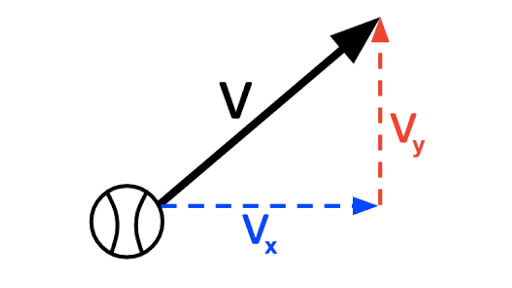
Speed is the magnitude of velocity. V 2 v x 2 v y 2.

Velocity Vectors 2 Calculating Velocity Given Speed And Direction Examsolutions Maths Revision Youtube
Velocity Acceleration and Time - Velocity calculations dont get any simpler than with this helpful online tool.

Resultant velocity khan academy. This problem is no exception. Gone are the days of looking up formulas and blasting away on your physical calculator with a notepad to figure out your problem. Speed andor direction we need to apply an overall resultant force to it.
Using the intermediate value theorem. An object that is in motion will not change its velocity unless an external resultant force acts upon it. Special thanks to the Physics Classroom for the development of these animations on this page.
Review these animations to describe motion using P-T and V-T graphs. When an object say a boat travels at a certain velocity and the medium through which it travels say a river has its own velocity we can find the resu. 4 False - if the resultant force is 0 then the object will not be moving.
Continuity at a point graphical Worked example. When an object say a boat travels at a certain velocity and the medium through which it travels say a river has its own velocity we can find the resultant velocity of the object by adding the two velocities. I suggest using the angle between.
V 08 ms 2 16 ms 2 v 18 ms. Resultant force Vectors Precalculus Khan Academy Homeroom with Sal Mala Sharma - Wednesday May 5. Vector word problem.
Average Velocity - EasyCalculation offers a great easy-to-understand way to find the average velocity for constant acceleration. Resultant velocity is the vector sum of all given individual velocities. In this example we find the resultant velocity vector of a boat.
The sum of the vector forces on an object is equal to the scalar product of the objects mass and its acceleration vector. Time volume density speed energy mass Vectors. The resultant velocity of an object is the sum of its individual vector velocities.
Point where a function isnt continuous. Velocity is a vector because it has both speed and direction. V V1 V2Vector Sum Ex.
Point where a function is continuous. In order to change the objects motion ie. Displacement velocity acceleration force moment momentum.
When an object say a boat travels at a certain velocity and the medium through which it travels say a river has its own velocity we can find the resultant velocity of the object by adding the two velocities. Resultant velocity Vectors Precalculus Khan Academy Vector word problem. Hello Natalia C The instantaneous speed the same applies to velocity is like the average speed but just for one instant of time.
Direction angles are often best determined using the tangent function. Describing Motion with Position-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs. If you want to know the average speed is it called so in English in a period of time you can determine it in the geometrical way by linking with a straight line the beginn and at the end of this period of time in the graph of the function.
In this example we find the resultant velocity vector of a boat. If the forces are balanced or non-existent then the objects motion does NOT change. Possess direction as well as magnitude and must obey the parallelogram law of addition and the triangle law.
Verifying inverse functions from tables. Our mission is to provide the world with free and easy-to-use calculators to solve your daily problems. The only thing open to discussion is our choice of angle.
An object that is at rest will stay at rest unless an external resultant force acts upon it. The step-by-step instructions and example problems encourage students to have fun learning the concept. The resultant force is 1000 N 775 N - 675 N - 1100 N 0 N so the object will not be moving.
Only magnitude is associated. There are many ways to calculate vector sums such as using a vector addition diagram but using trigonometry to calculate vector components is usually more efficient. Determining the resultant velocity is a simple application of Pythagorean theorem.
Perfect for students of all ages.

Velocity Vectors Calculating Speed Exercise Examsolutions Maths Revision Youtube

Physics Introduction To Vectors Part 1 Physics Introduction Addition Problems

Relative Velocity And Riverboat Problems Physics Classroom Ap Physics River Boat

Vedic Math Tutorial Tamil Youtube Math Tutorials Math Vedic
What Are Velocity Components Article Khan Academy

Instantaneous Speed And Velocity One Dimensional Motion Physics Khan Motion Physics Subbing Ideas Physics
What Are Velocity Components Article Khan Academy

Vector Word Problem Resultant Velocity Vectors Precalculus Khan Academy Youtube

Relative Velocity Swimmer Crossing A River Examsolutions Youtube

Pin By Melissa Hofmann On Library Physics Week 1 2 Worksheets Teaching Methods Physics

Relative Velocity Basic Introduction Youtube

Vectors Converting Velocity Into Speed Youtube

Resultant Ground Velocity Vector Application Youtube

Relative Velocity In 2d Video Khan Academy

Relative Velocity Rolling Wheel Youtube

Calculating Relative Velocity Video Khan Academy



Post a Comment for "Resultant Velocity Khan Academy"